The Importance of Professional Networking
The Importance of Professional Networking
You open your inbox and there is an invitation to attend an event or alternatively, you receive a formal invitation in the mail. So you gingerly place the invitation on the side or in a pending file, or you may even throw it away without a second glance. If it’s an Evite, you may respond and say you cannot attend. But you’ll never know what opportunities may have awaited you.
My professors and bosses have always stressed the importance of networking, and I couldn’t agree with them more. The old saying, “It’s not what you know, it’s who you know” holds a lot of truth.
Here are some reasons why professional networking is important:
Developing Relationships is Critical to Success
Developing and cultivating relationships is critical to success. People do business with those they know, like, and trust. It takes time, energy, and effort to build a network. Through building that network you develop and cultivate relationships with people who know you, trust you, and will do business with you.
Increases Your Chance of Getting a Job
In today’s current economic climate, the job market is very challenging and competitive with going up against potentially hundreds of other candidates for a single position. Constant rejections and lengthy interviews can sometimes mean that your face becomes just another in the pile. Just as networking with specific businesses can help you find your next job, so too can networking with industry recruiters. Often employers and industry recruiters have the inside scoop on possible new job openings before they are advertised. Employers prefer to hire based on referrals or recommendations which people in your network can provide. Managers and recruiters looking to fill a position will first search their own networks for candidates before the job goes public. Gaining access to these key players and hiring managers is tied directly to your network.
Increases Confidence Levels
Networking increases confidence levels because it will help you to push yourself to talk to people you don’t know. We cannot build strategic partnerships or social relationships unless we communicate. No matter what walk of life we pursue, we need to be able to break the ice, approach strangers and start, build, and maintain conversations. The more you do this, the easier it will become.
Allows for Visibility and Presence
Networking allows you to be visible and present. Instead of hiding in your cubicle or office, networking ensures that you are visible so the people in your organization know who you are. In each of my positions, I actively networked at all levels in the organization in order to develop positive relationships and create value for others in the company by being knowledgeable, reliable and a supportive person. Being visible and getting noticed is a big benefit of networking.
Who Should Be In Your Network?
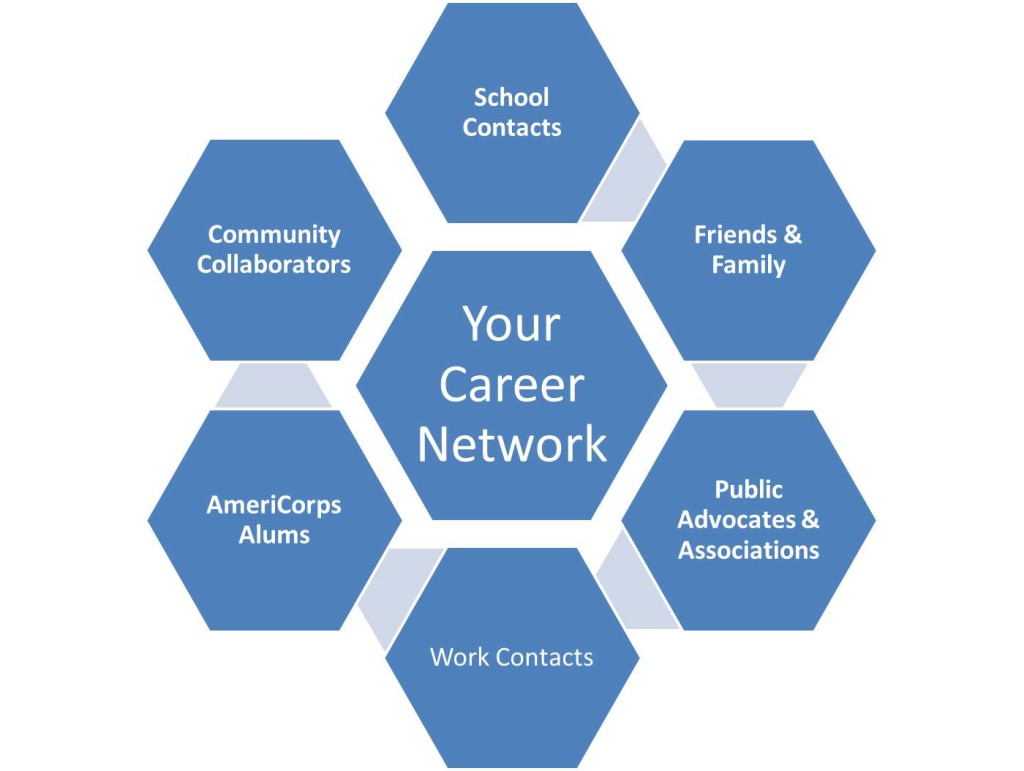
Your network can be made up of almost anyone you’ve ever met and each of your contacts can lead you to new ones such as:
- Current and Former Co-Workers: Those you currently work with as well as those you’ve worked with in the past can be part of your network.
- Your Co-Members in Professional Associations: When you become an active member in a professional association, you will increase your chances of meeting people. It will also give your colleagues a chance to see you in action.
- Friends and Family: Keep your family and friends apprised of your career goals. You never know who will end up having the ability to help you.
- Former Professors and Instructors: Your former professors and instructors most likely worked in your field or at least have some connections.
- Former Classmates: The alumni directory of your college can provide you with contacts to add to your network.
In conclusion, when your invitation arrives, gladly accept the invitation, and attend the event. These events give us a chance to meet new people and cultivate lasting relationships. With practice, you will be able to mingle while increasing your confidence level.

 managers have an ethical obligation to conduct employee appraisals in the most impartial and unbiased way possible. Researchers have recently distinguished two different types of performance appraisals: one based on the rational and the other based on the political perspective. The rational approach is designed to use objective criteria to assign accurate ratings. The goal of the political approach is subjective in nature and can use ambiguous standards which are designed to increase the degree of latitude provided to a manager when evaluating an employee. Prior studies have found that many managers have manipulated the performance appraisal process for political purposes. To reduce employee discord and workplace dissonance, managers have been found to give higher ratings to employees to keep them content. Higher ratings can also be given to obtain a promotion for preferential employees. Lower ratings can often be given to employees as a signal that they are no longer held in high esteem by the organization and it may be time to seek employment elsewhere. Low ratings can also be given by managers as a form of retaliation. However, lower ratings can be detrimental to employers because it can lead to decreased motivation, increased turnover, and increased risk of litigation.
managers have an ethical obligation to conduct employee appraisals in the most impartial and unbiased way possible. Researchers have recently distinguished two different types of performance appraisals: one based on the rational and the other based on the political perspective. The rational approach is designed to use objective criteria to assign accurate ratings. The goal of the political approach is subjective in nature and can use ambiguous standards which are designed to increase the degree of latitude provided to a manager when evaluating an employee. Prior studies have found that many managers have manipulated the performance appraisal process for political purposes. To reduce employee discord and workplace dissonance, managers have been found to give higher ratings to employees to keep them content. Higher ratings can also be given to obtain a promotion for preferential employees. Lower ratings can often be given to employees as a signal that they are no longer held in high esteem by the organization and it may be time to seek employment elsewhere. Low ratings can also be given by managers as a form of retaliation. However, lower ratings can be detrimental to employers because it can lead to decreased motivation, increased turnover, and increased risk of litigation.